Suppose your organization is drowning in heaps of emails and support tickets, social media feedback, and PDF files containing information about customers. It is good information, but it is disseminated everywhere like puzzle pieces falling on the floor. Sound familiar?
You’re not alone. According to recent research, about 80-90% of the data stored in an enterprise is not organized, whereas the majority of the business intelligence tools can only process structured data. Then it is like keeping a chest of treasure which you cannot unlock because you do not have the key.
The good news? It is not only possible to convert unstructured text into structured datasets but, each day, it is becoming more necessary and simpler to do so. Whether you need to analyze customer sentiment, derive insights using research papers or simply derive meaning out of legal documents, knowledge on how to bridge the gap between structured and unstructured data can change the way your organization functions.
Let’s dive into the methods, tools, and real-world challenges of turning text chaos into organized, actionable data.
Table of Contents:
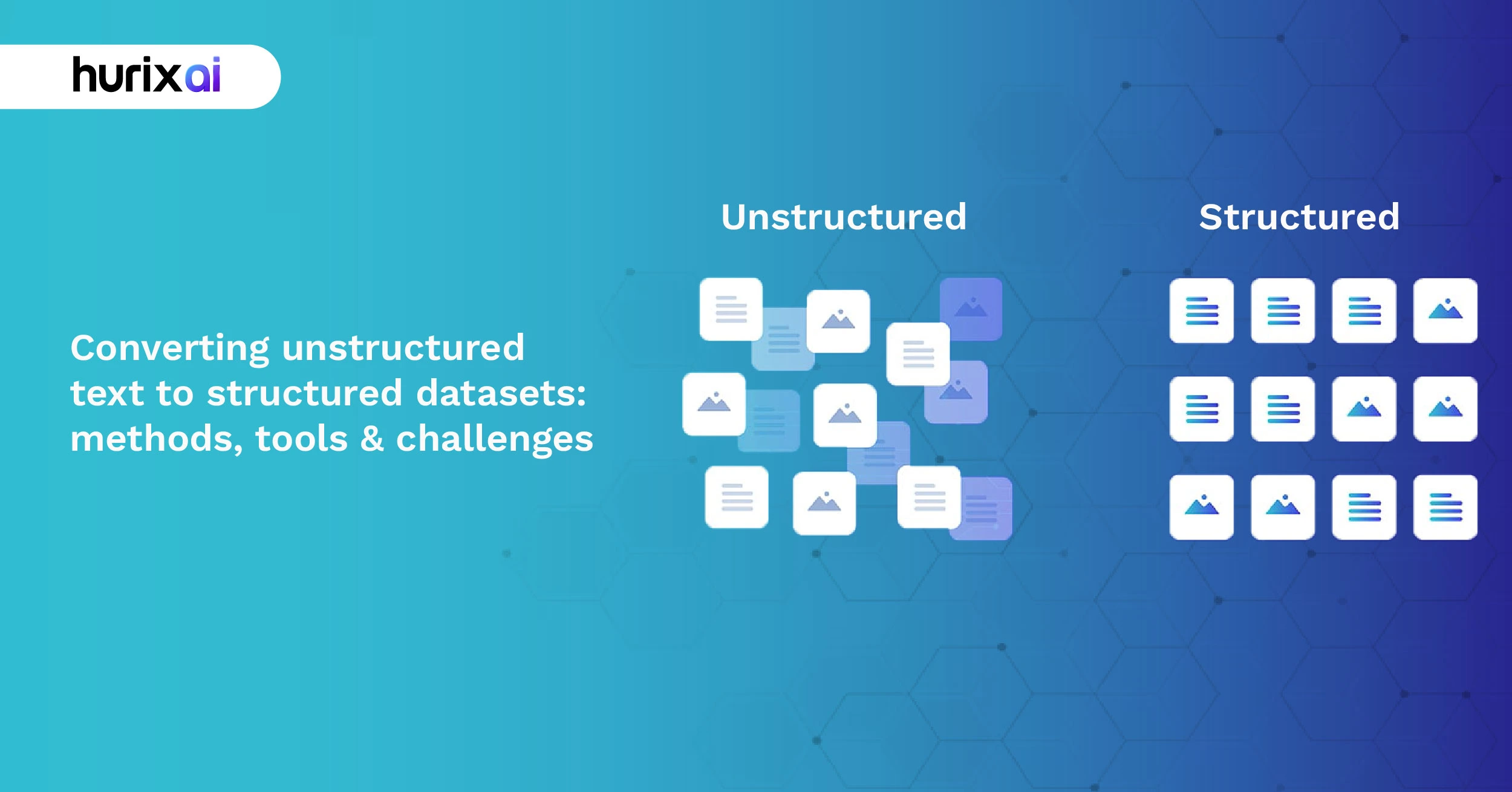
- What Is the Difference Between Structured and Unstructured Data?
- Why Should You Convert Unstructured Text into Structured Formats?
- 7 Proven Methods to Transform Unstructured Text into Structured Datasets
- What Are the Best Tools for Converting Unstructured to Structured Data?
- 5 Major Challenges When Structuring Unstructured Text Data
- When Should You Invest in Unstructured Data Conversion?
- Getting Started: Your Next Steps
- Transform Your Unstructured Data into Strategic Assets
- Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What Is the Difference Between Structured and Unstructured Data?
We should first make things straight about what we are talking about before we talk about conversion.
Structured data is the organized child at school. It exists in orderly rows and columns, adheres to established formats, and gets along with databases. Consider spreadsheets, SQL databases or customer relationship management systems. Every bit of information has its place and locating what one wants is easy. The sales records of your company with columns of date, product, quantity and revenue? That is the way structured data has its way.
Unstructured data, on the other hand, is the creative outcast. It is not rule bound and does not exist within categories. We are discussing emails and social media posts, telephone call transcripts, medical notes, contracts, and video materials. It is information with drastically useful information, but one needs more advanced methods to extract this information. Whenever a customer tweets about your product or a doctor leaves clinical notes, it is a highly information-dense but entirely unstructured.
At this point it is interesting; the arrangement of structured and unstructured data is not antagonistic, but rather complementary. When tied to the descriptions of their support tickets (unstructured), what was already a valuable customer ID (structured) will be invaluable. The magic is that you are able to transform one form into the other and that provides a whole picture of your data landscape.
Why Should You Convert Unstructured Text into Structured Formats?
It is not necessary to ask why should you. but instead “can you not afford not to?
Unleash Business Intelligence: Those stack of customer feedback emails are not a waste of paper, those are treasure troves of product enhancement tips, service voids and market trends. As it is organized, sentiment can be quantified, common themes can be determined, and emerging issues can be tracked and prevented before turning into a problem. One retailer company found that there was a bug with thousands of customers by simply organizing and analyzing their unstructured support tickets.
Make Data Analysis Actually Possible: Attempt to do a meaningful analysis of 50,000 untyped text files. I’ll wait. Conventional analytics systems and visualization systems require structured information to work. By transforming unstructured text to structured datasets, you can all of a sudden open the door to the world of statistical analysis, machine learning models, and predictive analytics. Your data scientists will appreciate you.
Improve Operational Efficiency: Document Review is a slow, costly and highly error prone manual procedure. Automating the unstructured data make the tasks that took days and weeks before computerized. Legal teams are able to quickly earmark significant clauses out of thousands of contracts. Millions of patient records can be analyzed by healthcare providers to determine their pattern of treatment. The saving of time will be turned into cost savings and quicker decision making.
Enable Better Decision-Making: When executives pose questions such as the one that reads: What are our customers saying about our new feature? or What are the regulations under this category of products? structured data is a good way to get a clear cutset amount of information. Decision-makers receive actionable insights, dashboards, and reports instead of reading hundreds of documents that need to be handled by hand.
Create Competitive Advantage: It is likely that your rivals are also perched on the same hills of unstructured pull. The first ones to be able to structure and analyze it are the ones that get much in terms of gaining insights into market dynamics, customer needs and failure in their operations.
The real question is: How much value are you leaving on the table by keeping your data unstructured?
7 Proven Methods to Transform Unstructured Text into Structured Datasets
Ready to roll up your sleeves? These are the time-tested strategies that are effective.
1. Rule-Based Text Processing
This is where you begin, this could be considered as teaching your computer to do what it is being asked to do. Pattern matching and regular expressions (regex) assist you in retrieving organized information in reasonable text formats.
As an instance, rules are just perfect when it comes to extracting email addresses, phone numbers, or dates out of documents. Assuming that invoices always include the text invoice Number: 12345 you can write a rule that will capture that text every time. The limitation? Regulations are violated when the text is unpredictable. There are no templates to customer reviews, and it is where you should resort to more advanced methods.
2. Named Entity Recognition (NER)
NER resembles a smart assistant that is able to find and label meaningful things in text. It identifies names of people, name of companies, addresses, dates, amounts of money and custom items that are important in your business.
The current NER systems rely on machine learning to comprehend the context. They understand that the word Apple in the sentence Apple announced new products is used to refer to a firm whereas the word apple in the sentence I ate an apple is used to refer to a fruit. NER is used by businesses to process contracts, news articles or research papers that used to be manually read to extract key entities.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP) Techniques
NLP represents a wide-ranging set of tools of human language. With tokenization, text is divided into words or phrases. Part-of-speech tagging recognizes adjectives, verbs and nouns. Dependency parsing shows the relationship between words.
These methods are useful to organize text with the knowledge of its grammatical and semantic elements. Combining them allows the more advanced analysis of, say, extracting subject-verb-object relations or finding out the major subjects in documents. Many other methods are possible on its basis.
4. Machine Learning Classification
Do you have thousands of documents that need categorizing? Machine learning classification gets to know through the examples you give it, and automatically categorizes new documents.
Provide a model with example of support tickets that have the tag of either technical issue or billing question or feature request, and they will automatically be classified. The beauty of the ML classification is that, it gets better as time goes and can handle subtle differences that rule based systems overlook. This is used to label the content by financial institutions to describe transactions, and by media companies to recommend content.
5. Information Extraction Templates
Templates generate schemas of a certain type of document. The extraction systems fill in the fields with unstructured text, since you define what you need (sender, date, amount, terms, etc.).
This is extremely effective in semi-structured documents such as invoices, receipts, forms and standard reports. The current template systems have adopted AI to manage a change in layout and formatting, change in vendor, change in document version or style of writing without manually coding each variation.
6. Sentiment and Emotion Analysis
Numbers matter, but so do feelings. Sentiment analysis structures subjective information by assigning scores or categories to text based on expressed emotions and opinions.
This method transforms “Your product is absolutely fantastic!” into structured data like sentiment: positive, confidence: 0.95, emotion: joy. Companies monitor brand reputation, analyze product reviews, gauge employee satisfaction, and track market sentiment by structuring emotional content at scale.
7. Large Language Models (LLMs)
The fresh faces in the block–and you know they are rather competent. Current LLMs such as GPT-4 are capable of contextual understanding, adherence to complex instructions, and heuristic information that was previously overlooked.
An LLM can be asked to extract all project deadlines, stakeholders, and risk factors in these meeting notes and give it out in structured JSON. They do deal with ambiguity, can read between the lines and operate in other fields without massive retraining. The tradeoff? They require computational resources and careful prompt engineering, but the results often justify the investment.
What Are the Best Tools for Converting Unstructured to Structured Data?
Theory meets practice here. Now, we should discuss the real tools that teams employ to do so.
Open-source NLP Libraries: spaCy and NLTK are the most popular Python text processors. They are strong, versatile and free. SpaCy is fastest in production workflow, whereas NLTK has detailed educational contents, research provisions. In cases of technical expertise teams, these libraries are offering the highest level of control and customization.
Plug-and-Play Cloud-Based AI Services: Google Cloud Natural Language API, Amazon Comprehend and Azure Text Analytics are the services that are offered as a plug and play. Send your text, make their APIs, and get data back in form. Ideal in companies that prefer the benefits of capabilities without necessarily developing infrastructure. They also manage scaling automatically and keep in pace with the current AI advancements.
Dedicated Data Extraction Engines: It has tools such as Import.io, Octoparse, and ParseHub are specifically designed to extract structured data on websites and documents. They have visual interfaces on the definition of extraction rules, thus available to non-programmers. Very useful to business analysts who do not have to write code to get results.
Enterprise Data Integration Suites: Informatica, Talend, and Apache NiFi provide all-purpose suites, which also embrace unstructured processing of data, in addition to the standard ETL processing. They are glowing in huge organisations whose data ecosystems are complex and need governance, security, and consolidation of various sources.
AI-powered Document Processing: UiPath Document Understanding, Rossum, and others deal with the processing of business documents. They are a combination of computer vision, NLP, and machine learning to process invoices, contracts, forms, and receipts with a minimal level of configuration.
Custom Solutions using Hugging Face Transformers: Hugging Face is accessible to the state-of-the-art language models, provided a team is developing a custom solution. You can also customize pre-trained models to your domain and get impressive results where generic tools have failed.
The appropriate tool will be based upon your technical capacity, size of data, budget and needs. Most companies combine cloud APIs to process everything, document-specific processing, and even unique models.
5 Major Challenges When Structuring Unstructured Text Data
Let’s be honest—this isn’t always smooth sailing. Here are the obstacles you’ll likely face and how to navigate them.
1. Data Quality and Inconsistency
Raw writings are sloppy in nature. Automated systems are put through headaches due to typo, shortening, slang, more than one language, and varied formats. Such customer feedback can be gr8 product or business lingo that your tools do not comprehend.
The answer: Invest in the data cleaning and preprocessing. Construct domain specific dictionaries. Exploit fuzzy matching variations. Learn to live with perfection:- set a goal that you consider to be good enough and keep at improving on it basing on actual results on the ground.
2. Context and Ambiguity
Language is marvelous and infuriatingly unclear. The bank to the left may be about a bank or the banks of a river. Apple can refer to the business, the fruit or a nickname of a person. Sentiment analysis is especially difficult because of sarcasm and idioms.
The solution: Utilize context-aware models that take into account the surrounding text. Implement human-in-the-loop validation for critical applications. Accept that automated systems won’t catch everything—build review processes for edge cases and high-stakes decisions.
3. Scalability and Performance
There is a lot of computation that is needed to process millions of documents. There are ways that are perfect on 1,000 documents that simply fall on 1,000,000. Latency is a problem when a real-time process is required.
The solution: Design with scale in mind from the start. Use distributed processing frameworks. Leverage cloud services that scale automatically. Optimize your pipelines—sometimes simpler methods that run faster are more effective than sophisticated methods that run slowly.
4. Domain Specificity
NLP models that are trained on general text have difficulties with specialized domains. Medical terms, legal terminology, technical and industrial jargon demand special knowledge. An out-the-box solution will crash on your specific text.
The solution: Fine-tune on your domain-specific data. Create industry specific entity recognizers. Look at special suppliers specializing in your industry. In some cases, the cost of domain expertise will save months of in-house development.
5. Privacy and Compliance
There is generally sensitive information in text data–personal information, health information, financial information, or trade secrets. The organisation of this data poses new risks. What occurs when your extraction unintentionally has your personally identifiable information? What do you do to make sure that you are GDPR or HIPAA compliant?
The solution: Implement data anonymization and redaction as part of your structuring pipeline. Conduct privacy impact assessments. Use on-premise solutions for highly sensitive data. Build audit trails showing how data was processed and who accessed it.
When Should You Invest in Unstructured Data Conversion?
Timing matters. Here’s how to know if you’re ready.
You’re ready when: Your team spends significant time manually reviewing documents. You’re making decisions based on gut feelings rather than comprehensive data analysis. Competitors are gaining advantages through better data utilization. You have valuable unstructured data sources, but lack visibility into them. Your current tools can’t answer important business questions because the data isn’t structured.
You’re not ready when: Your data volume is tiny and manual processing is genuinely faster. You lack clear use cases for the structured output. Your organization isn’t prepared to act on insights derived from the data. You’re treating this as a technology project rather than a business transformation.
The sweet spot hits when the value of insights locked in unstructured data clearly exceeds the investment in extraction and structuring. Begin with a pilot project that targets a specific, high-value use case. Prove the concept, demonstrate ROI, then expand.
Getting Started: Your Next Steps
Converting unstructured text to structured datasets isn’t a one-time project—it’s an ongoing capability that becomes increasingly valuable over time.
Start by identifying your highest-value unstructured data sources. What information, if structured and analyzed, would most impact your business? Begin with a focused pilot targeting that specific challenge. Utilize existing tools and services rather than building everything from scratch initially. Measure results clearly so you can demonstrate value and justify expansion.
Remember that perfection is the enemy of good. Your first structured datasets won’t be flawless, and that’s okay. The goal is progress, not perfection. Each iteration teaches you about your data, your needs, and the tools you use. Over time, your capabilities mature, and your returns multiply.
The organizations winning with data today aren’t necessarily those with the most sophisticated technology—they’re the ones who successfully bridge the gap between structured and unstructured data, creating unified views that drive better decisions.
Transform Your Unstructured Data into Strategic Assets
The difference between data-rich and insight-rich organizations often comes down to one capability: knowing how to connect structured and unstructured data in a way that makes information usable, measurable, and actionable. It’s not about collecting more data. It’s about making sense of what you already have.
Whether you’re drowning in customer feedback, buried under contracts, or struggling to extract value from years of accumulated documents, the methods and tools exist to transform that chaos into clarity. The question is whether you’ll take action while competitors are still manually reading through their text files.
Ready to unlock the value hidden across your structured and unstructured data landscape? At Hurix.ai, we help organizations transform messy text into strategic assets. Our AI-powered solutions cover everything from intelligent document processing to custom NLP pipelines, all tailored to your industry, your data, and your real-world challenges.
Let’s discuss what’s possible when your data works for you, rather than against you.
Contact us today. Don’t let valuable insights remain trapped in unstructured text. Your competitive advantage is waiting to be structured.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It depends entirely on your data volume and complexity. A small pilot project processing a few thousand documents might take 2-4 weeks from setup to results. Enterprise-scale implementations handling millions of documents across multiple formats could take 3-6 months to fully deploy. The good news? Modern cloud-based tools can start delivering value within days for straightforward use cases. The key is starting small with a focused application, proving value quickly, then scaling up based on results.
Absolutely! Many modern platforms offer no-code or low-code interfaces specifically designed for business users. Tools like Microsoft Power Automate, cloud AI services with visual interfaces, and specialized document processing platforms let you configure extraction rules, train models, and process data without writing a single line of code. That said, having technical support helps when you encounter complex scenarios or need custom solutions. The sweet spot for many organizations is pairing business users who understand the data with technical teams who can handle edge cases.
Accuracy varies dramatically based on your method, data quality, and use case. Simple extraction tasks like pulling dates or invoice numbers from standardized documents can achieve 95-99% accuracy. More complex tasks like sentiment analysis or extracting information from highly varied text typically range from 70-90% accuracy. Here’s the reality check: you’ll rarely hit 100% accuracy with automated systems. That’s why successful implementations build in human review for critical decisions and continuously improve models based on feedback. Start by measuring your current manual accuracy—automated systems often match or exceed human performance while processing exponentially more data.
This is a classic ROI question. Historical data conversion makes sense when those archives contain valuable insights, regulatory requirements mandate retention and accessibility, or you’re training machine learning models that benefit from more examples. Many organizations take a hybrid approach: structure all new incoming data automatically, then selectively convert historical archives based on business value. Ask yourself: “What decisions could we make better if we understood patterns in our historical data?” If the answer is compelling, conversion is worth it. If historical data is rarely referenced and has minimal strategic value, focus your resources on new data instead.
Quality maintenance requires ongoing attention, not just one-time effort. Implement validation rules that flag suspicious values or missing required fields. Build feedback loops where end users can report errors, which then improve your extraction models. Schedule regular audits comparing automated extraction against manual review samples. Monitor accuracy metrics over time—if performance degrades, investigate whether your source data has changed or your models need retraining. Most importantly, treat data quality as a continuous improvement process rather than a checkbox. Organizations that excel at structured data quality typically dedicate specific team members to data stewardship, ensuring someone owns the ongoing health of your converted datasets.

Vice President – Content Transformation at HurixDigital, based in Chennai. With nearly 20 years in digital content, he leads large-scale transformation and accessibility initiatives. A frequent presenter (e.g., London Book Fair 2025), Gokulnath drives AI-powered publishing solutions and inclusive content strategies for global clients